DNS BIND firewall settings
Allowing DNS traffic through the firewall is another important task to be completed when configuring your server.
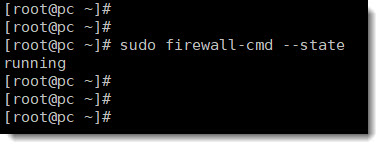
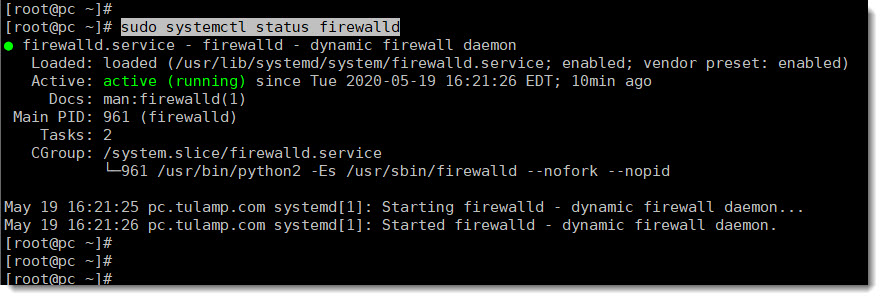
Firewall current state
First of all, use one of the following two CLI commands to see the current state of the firewall.
firewall-cmd --statesystemctl status firewalldDNS BIND ports
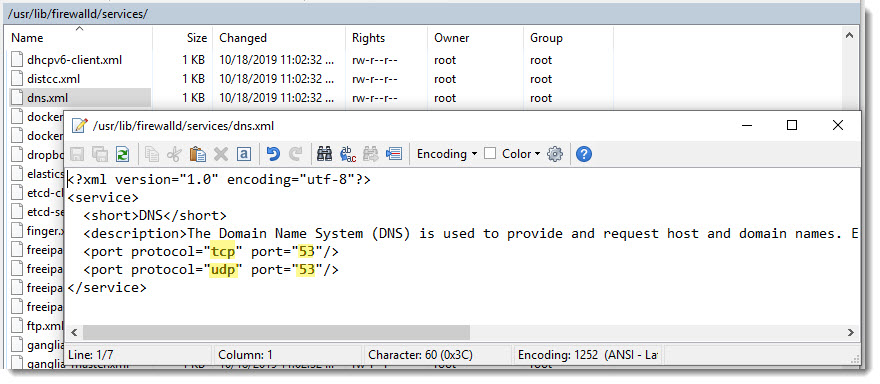
You’ve probably noticed when working with the “named.conf” file on the line number 13th(IPv4) and also on line number 14th(IPv6) that port 53 is mentioned there, that’s the default DNS port, you can also check that port via the firewall XML services file, that is located at the following path.
/usr/lib/firewalld/services/dns.xmlDNS BIND firewall exception
Both network and host firewalls must allow incoming TCP and UDP traffic over the port 53, standard DNS requests occur over UDP port 53, however, if the response size is over 512 bytes, as the case may be with DNSSEC, the request will need to be sent over TCP port 53.
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=dnsReload firewall
The firewall must be reloaded for the changes to take place, use the following CLI command.
firewall-cmd --reloadVerify DNS was added into the firewall exceptions
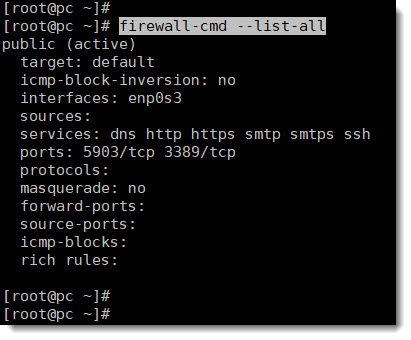
Use the following CLI command to see all the services that are currently allowed through the firewall and look to find DNS between them.
firewall-cmd --list-all